Electrification Indicators
EO Capability Benefits
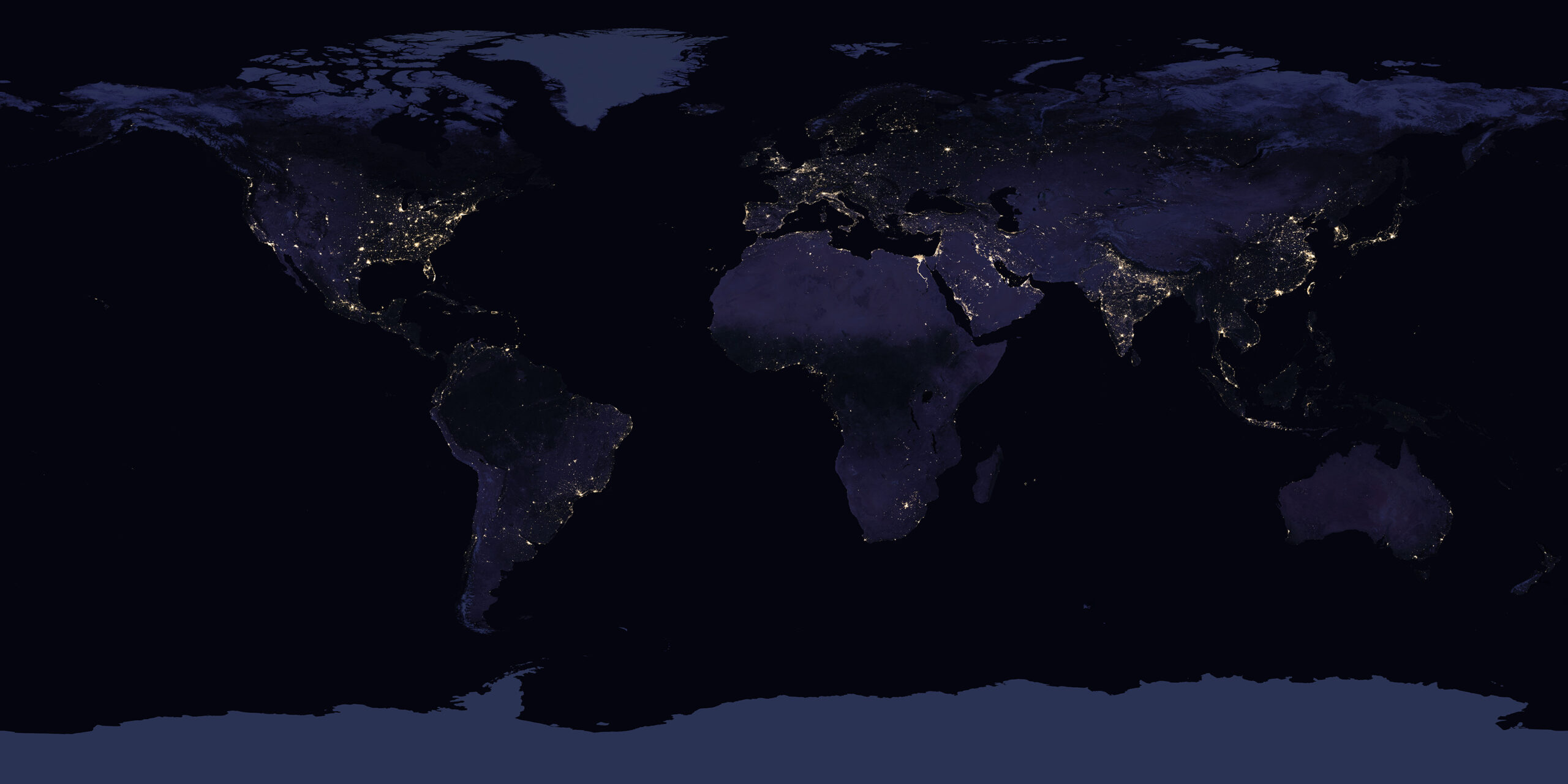
Earth Observation allows planners and policy-makers to use electrification proxies such as nighttime light data to monitor electrification in rural and urban areas, identifying underserved regions, and tracking temporal changes in electricity access. In 2022, UNDP, in collaboration with the University of Michigan, estimated using night-time lights and census data that 1 billion people in 100 countries lacked access to electricity.
EO Capability Description
Night-time satellite imagery, such as data from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) measures brightness levels at a 750m spatial resolution. This can be used to monitor electrification progress. Brightness intensity is correlated with electricity access and usage. These datasets can then be overlaid with Population Density products (itself using Built-Up Extent, Land Use Land Cover and a Digital Elevation Model as inputs) to predict unelectrified areas, particularly in rural regions. Challenges here include distinguishing between light sources powered by grid electricity versus diesel generators, especially in remote areas.
Energy Network and Infrastructure datasets which, for instance, map the location (and potential tilt) of power transmission towers can serve as secondary indicators of electrification progress. Similarly, datasets on the Solar Potential of Buildings can be compared with the deployment of existing rooftop solar PV to identify future growth areas.